

Line of Symmetry – A line that divides a figure into mirror images. Symmetry – a figure is symmetrical when one side of the figure is a mirror image of the other side. Trapezoid-a quadrilateral that has exactly one pair of parallel sidesĭiagonal-a segment that connects two vertices that are not next to each other Square-a parallelogram with four right angles and four congruent sides Rhombus-a parallelogram with four equal sides R Rectangle-a parallelogram with four right angles O Opposite sides and Opposite Angles-angles and sides that lie across from each other R Regular Polygon-a polygon with all sides and all angles congruent Parallelogram-a quadrilateral with both pairs of opposite sides parallel Similar figures – have congruent corresponding angles and the rations of the lengths corresponding sides are equal Polygon-a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that do not cross.Ĭongruent– having the same size and shape.Ĭorresponding sides and angles-The matching sides and angles of similar or congruent figures Of rectangular and triangular prisms and write their definitions. Use laminated flash cards of different types Write a description of how toįind the area of different two-dimensional and three-dimensional figures. Use handouts of formulas for finding surface area of rectangular and triangular prisms. Of the room for reference and review of concepts. There are ongoing visuals (laminated cards), which are kept on the board in the front Students are involved in team-tasks so that workĪnd learning are done in groups. The desks are arranged in groups of four or five students per group.
#Volume of triangular prism lesson how to#
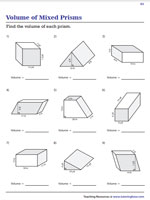
Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems. Represent three-dimensional figures using nets made up of rectangles and triangles, and use the nets to find the surface area of these figures. Apply these techniques in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.Ĥ. Draw polygons in the coordinate plane given coordinates for the vertices use coordinates to find the length of a side joining points with the same first coordinate or the same second coordinate. Apply the formulas V = l w h and V = b h to find volumes of right rectangular prisms with fractional edge lengths in the context of solving real-world and mathematical problems.ģ. Find the volume of a right rectangular prism with fractional edge lengths by packing it with unit cubes of the appropriate unit fraction edge lengths, and show that the volume is the same as would be found by multiplying the edge lengths of the prism.


Solve real-world and mathematical problems involving area, surface area, and volume.Ģ.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
